Feasibility Study Guideline for Public Private Partnership Projects
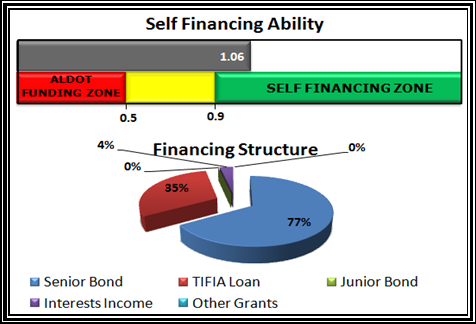 For many state Departments of Transportation (DOTs), a shortage of transportation funds requires the
agencies to combat that shortage by implementing innovative programs. Nationwide, Public Private
Partnerships (PPP) in transportation projects are increasingly gaining acceptance as an alternative to the
traditional approaches of project delivery and public financing. Due to the complexity of scale of PPP
projects, it remains a challenging task for state DOTs to identify PPP opportunity while protecting public
interest. This research presents a framework for PPP feasibility study at the early phase of project
development. The financing analysis process model is developed and refined for the guideline. An Excelbased
software package named P3FAST is developed and attached with the research report to facilitate
the PPP feasibility study for transportation agencies. An example is discussed to demonstrate the analysis
process and outcome. Three types of PPP models are compared and evaluated to achieve a feasible
financing structure. The report includes two volumes: volume I research report and volume II feasibility study guideline.
For many state Departments of Transportation (DOTs), a shortage of transportation funds requires the
agencies to combat that shortage by implementing innovative programs. Nationwide, Public Private
Partnerships (PPP) in transportation projects are increasingly gaining acceptance as an alternative to the
traditional approaches of project delivery and public financing. Due to the complexity of scale of PPP
projects, it remains a challenging task for state DOTs to identify PPP opportunity while protecting public
interest. This research presents a framework for PPP feasibility study at the early phase of project
development. The financing analysis process model is developed and refined for the guideline. An Excelbased
software package named P3FAST is developed and attached with the research report to facilitate
the PPP feasibility study for transportation agencies. An example is discussed to demonstrate the analysis
process and outcome. Three types of PPP models are compared and evaluated to achieve a feasible
financing structure. The report includes two volumes: volume I research report and volume II feasibility study guideline.
Innovative Contracting Strategies for Combating Climate Change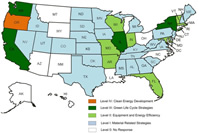
This project is sponsored by Maryland State Highway Administration. The state of Maryland has made a strong commitment to combating climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This research investigated the state of the art and practice of innovative contracting solutions to reduce emissions from highway construction activities. Implementation methods and challenges were identified and reported. Especially, the report presents a framework of green performance contracting (GPC) that includes four levels of strategies, namely material related strategies, equipment and energy efficiency related strategies, green life-cycle strategies, and clean energy development strategies. A total of 19 GPC strategies and their application procedures and cases were identified and documented. An optimization model based on the Data Envelopment Analysis was developed to assist state highway agencies to select appropriate green performance contracting strategies in accordance with environmental performance, organizational readiness, cost effectiveness, and other criteria. Implementation recommendations were provided to tackle climate change at the project level.
Design of Public Private Partnerships
Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) can be defined as "An agreement between the public and private sectors for the delivery of a project in which the private partner has the responsibility for acquiring the majority of the necessary financing and involve the private sector in nontraditional areas of a project with risks and rewards shared in new ways". Countries like United Kingdom and Australia have used PPPs extensively and effectively for developing public infrastructure. In comparison, the US PPP program is relatively new. The recent depletion of Highway Trust Funds in the US has forced the public agencies to arrange funds using non-traditional methods including PPPs. However, the increased involvement of private sector in public projects has invoked skepticism since it is felt that the use of PPPs does not warrant protection of public interests. This research addresses this issue and presents robust optimization models to design different aspects of PPPs. The research introduces
- a service selection model,
- a robust optimization model for structuring PPP finances and
- a model to design Availability Payment mechanism for PPPs.
Transaction Cost of PPPs
Due to limited financial resources of governments, Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as one of the most important ways of delivering infrastructure projects. Compared to traditional delivery approaches, PPPs bundle complex investments and service provisions with different project entities in a single long-term contract. Because of these special characteristics, many transactions happen during the life cycle of a PPP project, resulting in an increase in "transaction cost" of the project. Transaction costs are known in economics as the costs associated with executing projects such as searching, negotiating, contracting and enforcing. Earlier studies show transaction costs in other industries are significant. This research covers a theoretical discussion about the definition of transaction costs and different factors affecting them. It reviews the current accounting systems that are used by different state DOTs and federal agencies that are involved in the procurement process of a PPP highway project. It develops a general PPP process flowchart for infrastructure projects in the US, and based on the mapping of PPP transaction activities to project cost items, presents a cost breakdown structure (CBS) as well as a cost coding system to enhance current accounting systems. This accounting model is further justified with two case studies about I-495 HOT lanes in Virginia, and I- 595 improvements project in Florida.
A Multi Objective Decision Support System to Enhance Funding Strategies in PPPs
PPP is an innovative delivery method used as an option to leverage public funds by attracting private investment into public projects to make the delivery of previously impossible projects possible. Leveraging resources to build more infrastructure increases the output (quantity) of funds; however, besides leveraging resources, the public agency should also increase the outcome (benefits) of those projects by utilizing more efficient funding strategies. Currently, some project level evaluation methods such as VfM and BCA are being practiced to evaluate PPPs; however, those methods fail to consider the overall benefits and costs of PPPs for multiple stakeholders, and they do not provide much assistance in terms of comparison between different projects in portfolio level. This study introduces a Multi-Objective Decision Support System (MODSS) which integrates quantitative and qualitative aspects of PPPs and calculates the utility function based on different interests of multiple stockholders. There are different key performance indicators that are defined under three main attributes: the ROR on private investment, the regional economic benefits and the long term national level benefits. This two level MODSS model assists public agencies such as FHWA to better spend their resources in special programs such as TIFIA by helping them in optimizing their funding portfolio by allocating the available funds into the optimal portfolio of PPP projects.
Construction Risk Evaluation and Relevant Policies for Chinese Large-scale Public Buildings
This project is a joint research with Southeast University and sponsored by Ministry of Housing and Urban- Rural Development of China. The final delivers cover eight specific reports including:
1. National-level risk evaluation system, based on the ASCE infrastructure report card;
2. Program-level risk evaluation system, based on 2008 Beijing Olympic Games construction program;
3. Project-level risk evaluation system, referred to PDRI (CII) guideline;
4. Risk allocation and risk checklist, referred to the ERA (CII) guideline;
5. Risk evaluation techniques review, referred to ISO IEC/FDIS 31010;
6. Specially topic: US K-12 school quality control and maintenance policies, based on the Maryland schools system
7. Specially topic: Review of US safety management and emergency management
8. Specially topic: Reference of US large-scale public buildings and infrastructure
A Decision Model for Technology Selection in Renovation Project Planning
As infrastructure ages, a significant portion of US capital expenditure is incurred for the renovation and retrofit of existing facilities. Renovation projects are complex, high risk, and involve extensive coordination and planning, primarily due to uncertain site conditions and continuing operation requirements of existing facilities. Early studies have identified innovative and emerging technologies that facilitate site investigation and align renovation and maintenance activities with business production and operation schedules. However, the selection of appropriate technologies in specific project and business environments remains a challenge. Particularly, there is no guidance for project teams who must incorporate the selected new technologies into scope management and project planning. This research establishes a framework to guide project teams towards appropriate technology selection in renovation project planning. A decision model is developed to integrate the technology selection process into a widely used scope management tool, Project Definition Rating Index (PDRI). The model is specially designed and flexible enough to allow project teams to decide appropriate technologies according to various criteria, including cost, application area, and risk mitigation.
Guarantee Design on Energy Performance Contracts under Uncertainty
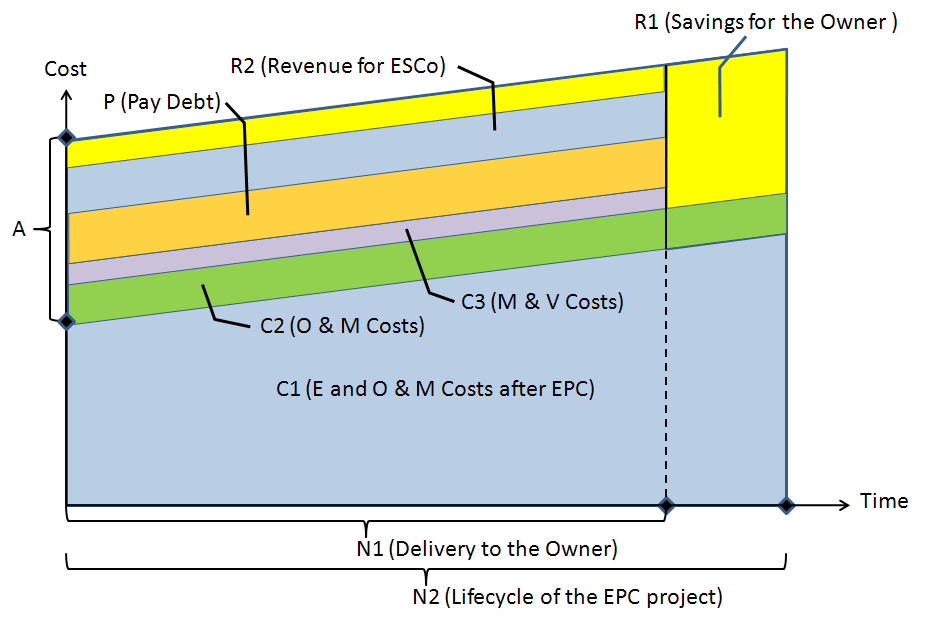 With the appearance of energy price increasing, resource scarcity and sustainable development problems, energy efficiency has become one of the quickest and cheapest ways to increase the amount of energy available for use. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, buildings account for about 40% of U.S. energy usage, and there are sufficient viable opportunities for energy-efficiency improvements to reduce carbon emissions and save money. Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) is such a turnkey building service that provides clients with a comprehensive set of Energy Conservation Measures (ECMs) and is often accompanied with guarantees that the savings produced by a project will be sufficient enough to finance the full cost of the project. Under EPC arrangement, Energy Services Companies (ESCOs) use the stream of income from future cost savings to repay their initial investments. However, few studies have examined how to set the guarantees or how to share the potential exceeding profit between ESCOs and the clients with fixed-price guarantees in EPC based on the existing annual energy savings estimation. In practice, the related contract items are often blurred or ignored by both the ESCOs and the clients. This research provides a more flexible energy savings guarantee designing method, considering the potential volatility risk of energy price and quantity. Having a better understanding on the contract specification could not only give a good reference on the optimal EPC bidder selection, future schedule and budget arrangements from the clients’ perspectives, but could also help ESCOs reasonably allocate the estimation financial risks with successful contract negotiation.
With the appearance of energy price increasing, resource scarcity and sustainable development problems, energy efficiency has become one of the quickest and cheapest ways to increase the amount of energy available for use. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, buildings account for about 40% of U.S. energy usage, and there are sufficient viable opportunities for energy-efficiency improvements to reduce carbon emissions and save money. Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) is such a turnkey building service that provides clients with a comprehensive set of Energy Conservation Measures (ECMs) and is often accompanied with guarantees that the savings produced by a project will be sufficient enough to finance the full cost of the project. Under EPC arrangement, Energy Services Companies (ESCOs) use the stream of income from future cost savings to repay their initial investments. However, few studies have examined how to set the guarantees or how to share the potential exceeding profit between ESCOs and the clients with fixed-price guarantees in EPC based on the existing annual energy savings estimation. In practice, the related contract items are often blurred or ignored by both the ESCOs and the clients. This research provides a more flexible energy savings guarantee designing method, considering the potential volatility risk of energy price and quantity. Having a better understanding on the contract specification could not only give a good reference on the optimal EPC bidder selection, future schedule and budget arrangements from the clients’ perspectives, but could also help ESCOs reasonably allocate the estimation financial risks with successful contract negotiation.
National Infrastructure Condition Evaluation and American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) Report Card Case Study
The condition of a nation’s infrastructure is a critical factor in determining civil and economic health. To sufficiently maintain an infrastructure system it is critical that it be continually evaluated. This paper discusses national level infrastructure evaluation strategies and evaluates the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) Infrastructure Report Cards from 1988 through 2009. Methods for classifying infrastructure evaluation as well as ways of determining its societal value are proposed. In addition, a four-level conceptual framework model of national infrastructure is presented. These concepts are then illustrated and critically evaluated with the ASCE 1988-2009 report cards. This research specially focuses on the condition of infrastructure at the national level rather than that of a single project. The purpose of this paper is to ultimately suggest a conceptual framework by which a nation can conduct a viable infrastructure assessment.
Renewable Energy Case Studies
 This research focuses on renewable energy projects implemented by state agencies, in particular those that use innovative contracting or financing strategies. Of interest are the Solar Highway developed by the Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT) and wind energy projects initiated by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MDOT). The Solar Highway features a 104-kilowatt solar photovoltaic system that consists of 594 solar panels and covers about 8,000 square feet. It was financed through a partnership with SolarWay, a renewable energy consortium that was able to capitalize on both federal and state energy incentives. These incentives are becoming a trend throughout the United States. As such in 2007, Massachusetts Governor Deval Patrick issued Executive Order 484, “Leading By Example – Clean Energy and Efficient Buildings” that set ambitious goals to deploy 250 MW of solar power by 2017 and 2,000 MW of wind power in Massachusetts by 2020. Numerous sustainable energy projects are being implemented from this executive order including the recently announced project that will install a 400 ft. tall 1.5 MW utility grade turbine at the Blandford Rest Area located along the Massachusetts turnpike in Hampden County.
This research focuses on renewable energy projects implemented by state agencies, in particular those that use innovative contracting or financing strategies. Of interest are the Solar Highway developed by the Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT) and wind energy projects initiated by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MDOT). The Solar Highway features a 104-kilowatt solar photovoltaic system that consists of 594 solar panels and covers about 8,000 square feet. It was financed through a partnership with SolarWay, a renewable energy consortium that was able to capitalize on both federal and state energy incentives. These incentives are becoming a trend throughout the United States. As such in 2007, Massachusetts Governor Deval Patrick issued Executive Order 484, “Leading By Example – Clean Energy and Efficient Buildings” that set ambitious goals to deploy 250 MW of solar power by 2017 and 2,000 MW of wind power in Massachusetts by 2020. Numerous sustainable energy projects are being implemented from this executive order including the recently announced project that will install a 400 ft. tall 1.5 MW utility grade turbine at the Blandford Rest Area located along the Massachusetts turnpike in Hampden County.