TOOLKIT P3FAST FOR THE PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS
To read more, access the Full Report here (contact Professor Cui for a trial version of the toolkit)
INTRODUCTION
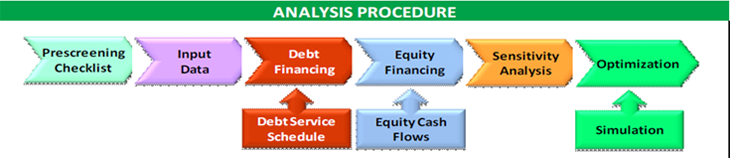
The Public-Private Partnership Feasibility Analysis Toolkit (P3FAST) is developed based on a PPP program framework that consists of organizational set-up, financing mechanism, PPP format, user fee approach, and procurement process, and provides guidance for public sector authorities in assessing the viability of a PPP project. The toolkit is based on a financial model which follows a four-step process to evaluate PPP opportunity, identify debt and equity needs, and determine financing structure. These steps are discussed below.
MODULE ONE: PROJECT PRESCREENING
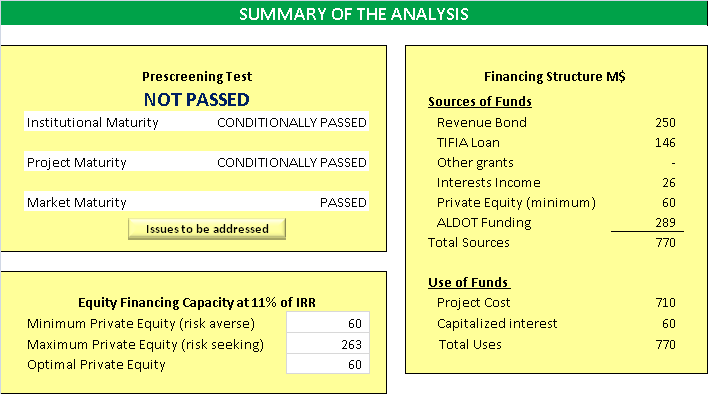
By analyzing three different aspects of a PPP candidate project - Institutional Maturity, Project Maturity and Market Maturity, this step helps state authorities to decide whether a project has potentials to be considered as a PPP project and what are the potential implementation barriers and risks. This pre-screening checklist analyzes three different aspects of a PPP candidate project - Institutional Maturity, Project Maturity and Market Maturity. Based on simple questions that will be asked in each category, it will suggest three different outcomes: “Passed,” “Conditionally Passed,” and “Not Passed.” The objective of the prescreening is to:
Evaluate PPP opportunities
Evaluate PPP maturity
Identify PPP implementation barriers and risks

MODULE TWO: DEBT FINANCING TEST
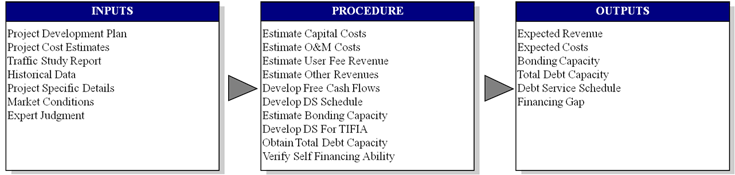
This module is designed based on the Debt Financing Test, a structured analysis to determine bonding capacity, verify self-financing ability, identify equity needs, develop debt structure, establish debt service schedule. This module requires inputs of estimates of capital costs, yearly operation and maintenance costs, user toll rates, inflation, user demand, revenue sources, traffic growth rate, pavement maintenance schedule, ramp up period details, truck percentage, truck toll rate, and Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR). The output of the module is the estimated project cash flows and debt capacity estimates. As the process completes, the module will provide answers to the basic question – Can the project finance through debts and other grants or will it require equity investment?
MODULE THREE: EQUITY FINANCING ANALYSIS:
The Equity Financing Analysis module follows the debt financing module and is conducted if debt is not enough to finance the project. This equity financing module provides information about the private equity investment in a project and whether or not public equity or subsidies is required to make the project bankable and attractive for private investors. This module is designed is to estimate the range of private investment, determine the rate of return on equity investment, and identify public funding requirement.
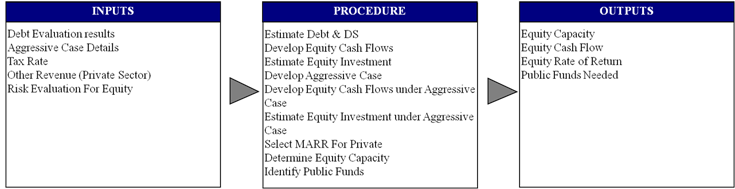
The equity financing test uses the debt capacity, free cash flow statements, and debt service schedules obtained as outputs from the debt financing test. The module produces an equity cash flow statement and calculates the possible equity investment in the project. The procedure further requires development of an aggressive case, which captures the gains expected by the private sector for taking higher risks. The procedure further requires the use of appropriate minimum acceptable rate of return (MARR), determination of equity capacity of the project, and the public equity in the project. Equity financing module provides equity capacity of the project, equity cash flows, and the public funds for the project as output.
MODULE FOUR: SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS & OPTIMIZATION:
Considering the complexity of PPP projects, this module is designed to evaluate the effect of different risk factors on analysis results, identify the risk mitigation priority, and determine the optimal capital structure under uncertainty. This module is capable of providing some sensitive data in graphical format to state officials in order to facilitate negotiations and decision making.
The optimization module is based on a linear programming algorithm which requires DSCR, total debt capacity, debt capacities of senior bonds, junior bonds, TIFIA, or any other bonds and debt service for each bond type; it also requires revenues under aggressive case and base case, minimum acceptable rate or return (MARR) for debt lending institutions, private investors and the state DOT, and long term plans of the department to estimate the opportunity loss coefficient as inputs. Optimization is carried out using Excel’s inbuilt solver. However, the revenue streams variable is a random variable in the model. Hence, simulations were used to obtain optimal capital structure assuming the revenue streams to follow beta distribution.
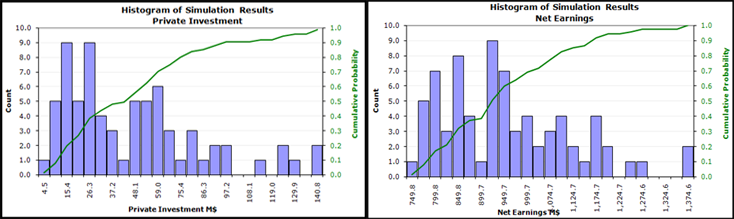
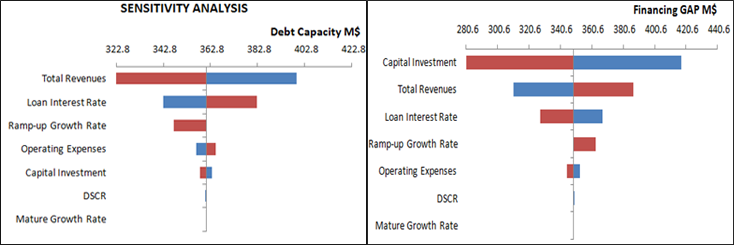
CASE STUDY DEMONSTRATION:
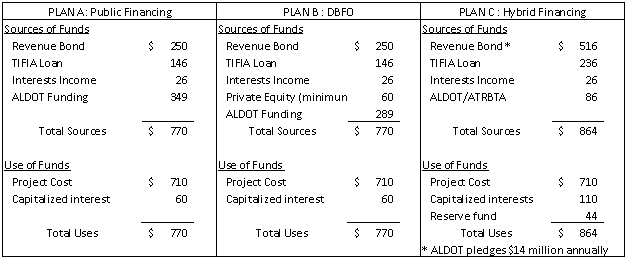
US Highway 280 travels through rural areas and smaller cities in southeastern Alabama to Birmingham. It has rapidly developed over the past 20 years and become a principal arterial serving commuter traffic and suburban development in southeast Jefferson County and northeast Shelby County. Given the limited capital budget available to ALDOT, one major issue associated with the US280 expansion project is to identify alternative funding sources. This paper focuses on the project financial analysis to demonstrate the process and outcome of proposed feasibility study guidelines. The analysis follows conservative assumptions to prevent overestimating project revenues and underestimating costs and uncertainties. Three financing plans are evaluated as follows:
Public financing scenario:
This Plan assumes the public financing scenario through a revenue bond secured against future net revenue, along with TIFIA funding.
DBFO:
Under plan B, a private company will finance and build the project, then get the investment back through toll collection within the concession period.
Hybrid financing:
A hybrid financing plan is also considered consisting of public financing and availability payment. Under this plan, ALDOT will pledge $14 million a year to the project for the entire loan term depending upon the performance and service level.